Sitemap
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Pages
Posts
[사이언스칼럼] 2025년, AI는 어떻게 진화했는가: 에이전트·평가·학습의 재정의
Published:
지난 1월 딥시크 R1 모델이 등장해 세상을 떠들썩하게 했다. 이 중국발 오픈소스 추론 모델은 오픈AI의 추론 모델인 o1과 견줄 만한 성능을 내며, 상대적으로 적은 비용과 알고리즘 효율화로도 최고 수준의 모델을 만들 수 있음을 보여주며 AI 산업의 판도를 뒤흔들었다. 그 충격파는 1년 내내 이어졌고, 2025년 AI는 눈부신 진화를 이루었다. 에이전트, 평가, 학습 및 스케일링의 진화라는 축에서 2025년을 되돌아보자.
[사이언스칼럼] AI 버블인가, 혁신의 전주곡인가
Published:
1990년대 말 닷컴 버블은 기술 낙관주의가 투기와 결합할 때 얼마나 위태로워질 수 있는지를 보여준 상징적 사건이었다. 당시 인터넷 기업들은 사용자 수만으로 기업 가치를 평가받으며 급등했지만, 수익 기반이 빈약했던 수많은 회사가 붕괴하면서 기술 거품의 본질이 드러났다. 그러나 흥미로운 점은 그 붕괴가 끝이 아니었다는 것이다. 거품이 꺼진 뒤 살아남은 기업들이 차세대 인터넷 경제의 주역이 되었다.
[사이언스칼럼] AI 에이전트 시대의 새로운 화두: 컨텍스트 엔지니어링
Published:
최근 거대언어모델(LLM) 의 진화 속도는 놀라울 정도다. 일상적인 글쓰기 보조부터 소프트웨어 개발, 데이터 분석에 이르기까지 다양한 영역에서 우리의 일과 삶에 실질적인 영향을 주고 있다. 이러한 LLM을 효과적으로 활용하기 위한 방법으로 ‘프롬프트 엔지니어링’의 중요성이 주목받아 왔다. 하지만 최근에는 스스로 복잡한 작업을 계획하고 실행하는 AI 에이전트가 등장하면서, 단순하고 정적인 프롬프팅을 넘어 ‘컨텍스트 엔지니어링’이라는 새로운 개념이 부상하고 있다.
[사이언스칼럼] 한국 AI 인프라의 미래: KAIRR을 제언한다
Published:
2025년, 대한민국 AI 생태계를 견인할 두 개의 초대형 엔진이 본격 가동된다. 하나는 초거대 AI 모델 개발에 특화된 국가 AI 컴퓨팅센터이고, 다른 하나는 과학기술 분야 계산과 AI 융합 연구를 담당할 KISTI 슈퍼컴퓨터 6호기다. 각각 1만 개의 최신 GPU와 8496개의 GH200 GPU를 탑재한 이 두 인프라는 한국 AI의 미래를 좌우할 핵심 동력이 될 것이다.
[사이언스칼럼] AI 에이전트의 새로운 진화: 마누스 AI와 MCP가 여는 미래
Published:
2025년 인공지능(AI) 기술은 또 한 번의 혁신적 도약을 맞이하며, 자율형 범용 AI 에이전트 시대의 문턱에 서 있다. 이 전환점을 이끄는 두 핵심 기술은 중국 스타트업 모니카가 3월 초에 선보인 마누스 AI와, 지난해 11월 앤트로픽이 AI 에이전트 데이터 교환 표준 기술로 공개한 후, 최근에 주요 AI 기업들이 자사의 에이전트 플랫폼에 채택하며 빠르게 확산 중인 모델 컨텍스트 프로토콜(Model Context Protocol, MCP)이다. 이 두 기술은 각각 자율성과 통합성의 측면에서 AI 생태계를 새롭게 재편할 잠재력을 가지고 있으며, 앞으로의 AI 응용과 서비스 방식에 지각변동을 예고한다.
[사이언스칼럼] 딥시크가 촉발한 글로벌 AI 민주화 불길, 한국의 미래는?
Published:
2025년 새해 벽두부터 중국발 딥시크 바람이 거세다. 속도 면에서 2년 전 챗GPT 열풍을 능가하는 딥시크 광풍이 전 세계를 강타하고 있다. 중국 AI 스타트업 딥시크가 공개한 딥시크-R1 모델은 오픈AI의 추론(reasoning) 모델인 o1과 견줄 만한 성능을 보인다. 특히 오픈소스로 공개돼서 모델을 다운로드 받아 목적에 맞게 모델 크기와 성능을 커스터마이즈하고 상업적으로 제약 없이 사용할 수 있게 됐다는 점에서 AI 산업의 판도를 뒤흔들고 있다. 또한, AI 모델 개발에 천문학적인 비용과 최첨단 반도체 자원이 필수적이라는 기존 인식을 깨고, 알고리즘 효율화로도 최고 수준의 성능을 달성할 수 있음을 입증했다.
[사이언스칼럼] AI 3대 강국 도약, 속도가 관건이다
Published:
지난 9월 26일 정부는 국가인공지능위원회를 출범하며 2027년까지 AI 3대 강국으로 도약하겠다는 비전을 선포했다. 이를 위해 국가 차원의 총력전을 펼치며 AI 인프라 확충을 포함한 4대 핵심 프로젝트를 실행하겠다고 밝혔다. 특히 필자의 관심을 끈 것은 수조 원 규모의 국가 AI 컴퓨팅센터 구축 계획이다. 정부는 2030년까지 엔비디아 최신 H100 GPU 3만 개 규모인 2엑사플롭스(EF) 이상의 컴퓨팅 자원을 확보하겠다고 한다.
[사이언스칼럼] AI 주권 경쟁 본격화, 국가 AI 슈퍼컴퓨터 구축 시급하다
Published:
지금 전 세계는 AI 주권을 확보하기 위한 치열한 경쟁을 벌이고 있다. AI 주권이란 국가나 조직이 인공지능 기술과 관련된 모든 측면에서 자율성과 독립성을 가지는 것을 의미한다. 단순히 기술을 보유하는 것을 넘어서, 자국의 언어, 데이터, 문화, 가치관을 반영한 초거대 언어 모델(LLM)을 자체적으로 개발하고 활용하는 것이 필수다.
[사이언스칼럼] 국가 차원의 최신 GPU 만 개를 확보하자
Published:
“GPU 없는 대학이 어떻게 진보를 이룰 수 있을까요?” 이미지넷의 창시자이자 세계적인 AI 석학인 스탠포드 대학의 페이페이 리 교수가 스탠포드대 인간 중심 AI 연구소(HAI) 창립 5주년 기념행사의 한 대담에서 던진 질문이다. 6월 5일 스탠포드 대학에서 HAI 출범 5주년 기념 컨퍼런스가 열렸다. 다양한 패널과 대담이 진행됐다. 위 질문은 페이페이 리 교수가 실리콘밸리 최고의 벤처캐피털 중 하나인 a16z의 마크 안드레센 공동창업자와의 대담 중에 나왔다. 마크 안드레센이 오늘날 AI 발전에 끼친 스탠포드와 MIT 같은 대학의 역할에 대해서 강조할 때 이에 페이페이 리 교수가 GPU 없는데 어떻게 대학에서 AI 연구를 할 수 있느냐는 반문이다.
[사이언스칼럼] AI 혁신의 열쇠, 국가 AI 슈퍼컴퓨터 구축 시급
Published:
인공지능(AI) 기술이 빠르게 진화하고 있다. 특히 챗GPT 이후 거대언어모델(LLM) 기술에 기반한 생성형 AI의 본격적인 등장은 새로운 시대를 열고 있다. 하루가 멀다 하고 챗봇, 번역, 이미지·비디오, 코드 생성 등 다양한 형태의 생성형 AI 서비스들이 출시되고 있으며 이는 의료, 교육, 예술 등 다양한 분야에 혁신을 가져올 것으로 기대된다.
[사이언스칼럼] 세계 AI 칸 페스티벌을 통해 만난 얀 르쿤 교수와 EU AI법
Published:
지난 2월 8일부터 10일까지 프랑스 칸에서 제3회 세계 AI 칸 페스티벌(WAICF 2024)이 개최됐다. 250여 개의 강연·토론 세션이 테크·전략, 응용, 데모, VC서밋 등 8개 카테고리로 나뉘어 진행됐다. IBM, HPE 등 글로벌 기업, INRIA 등 연구소 그리고 AI 스타트업들의 230여 개의 전시부스가 마련돼 성황리에 열렸다. WAICF 마지막 날인 토요일은 ‘오픈데이’ 행사로 전시장을 무료로 개방해 일반인들도 강연과 다양한 AI 첨단 기술을 체험할 수 있게 했다. 많은 비가 내리는 궂은 날씨에도 삼삼오오 아이들 손잡고 온 가족들의 모습이 인상적이었다.
[사이언스칼럼] 2023 슈퍼컴퓨팅 컨퍼런스를 통해 보는 글로벌 동향과 한국 현황
Published:
2023년 11월 12일부터 17일까지 슈퍼컴퓨팅 컨퍼런스(SC23)가 미국 덴버에서 개최됐다. 1988년부터 미국에서 열리는 연례행사로 고성능컴퓨팅, 네트워킹, 스토리지, 데이터 분야의 최신 기술을 교류하는 세계 최대 국제행사다. 2020년 코로나 팬데믹 이후 처음 온전히 오프라인으로 치러진 이번 행사에 1만 4000여명이 참석하고 438개의 전시부스가 마련되는 등 성황리에 열렸다. 한국도 한국과학기술정보연구원(KISTI), 한국반도체산업협회, SK하이닉스, 망고부스터, 프랜들리AI 등 연구소, 산업협회, 대기업, AI 스타트업 등 예년보다 다양한 기관에서 전시부스로 참가해 열기를 더했다.
[사이언스칼럼] 대형언어모델(LLM) 시대의 도전과 기회
Published:
LLM 춘추 전국시대다. 세계 최대 AI 모델과 데이터 공유 오픈소스 플랫폼 허깅페이스에서 운영하는 LLM 성능 순위를 매기는 ‘오픈 LLM 리더보드’의 톱 순위가 며칠을 멀다하고 바뀌고 있다. 8월에 한국의 스타트업 업스테이지의 LLM이 세계 1위를 차지하는 쾌거를 올렸다. 9월 초에는 아랍에미리트(UAE) 과학연구센터첨단기술연구위원회(ATRC)의 기술혁신연구소(TII) 팰컨 180B(매개변수 1800억 개) 모델이 리더보드 정상에 올랐다. AI의 변방인 UAE에서 GPT-3(매개변수 1750억개) 크기의 사전학습 LLM을 개발한 것이 놀랍다. ATRC의 TII는 지난 5월 상업용 오픈소스 사전학습 모델의 첫 사례 중 하나인 팰컨 40B을 정상에 올리면서 세계적인 주목을 받았다.
[사이언스칼럼] 거대언어모델, 오픈소스와 빅테크 간 대결의 최종 승자는
Published:
챗GPT 이후 거대언어모델(LLM)에 기반한 챗봇, 번역, 이미지 및 비디오, 코드 생성 등 생성 AI 서비스가 점점 일상화되고 있다. 최근에는 하루가 멀다 하고 개인 PC에서도 실행할 수 있는 소형의 가성비 좋은 오픈소스 LLM이 쏟아져 나오고 있다. 마이크로소프트(MS), 오픈AI, 구글과 같은 빅테크들의 LLM 기술 독점과 유로 API 서비스에 따른 오픈소스 진영의 반격이다.
[사이언스칼럼] 스탠포드大 ‘AI 인덱스 2023’ 보고서로 읽는 글로벌 AI 트랜드
Published:
4월 초에 스탠퍼드대 인간중심 AI 연구소(HAI)의 386쪽 ‘AI 인덱스 2023’ 보고서가 발표됐다. 이 보고서는 2017년부터 매년 발간되며 연구개발·기술·투자·교육 등 다양한 분야의 AI 관련 데이터의 수집·분석을 통해서 글로벌 AI 추세와 동향을 발표한다. 온라인 가시화 툴을 통해 AI 고용 지수와 저널 논문 출판 수 등 20여개 지표에 대해 약 30개 국가 간 순위를 볼 수 있어서 글로벌 대비 한국 AI 현주소도 파악할 수 있게 해준다.
[사이언스칼럼] 美, 국가 AI 연구 인프라 구축 실행 계획 발표와 시사점
Published:
챗GPT 광풍이 거세다. 지난 1월 초 필자는 ‘초거대 AI 언어모델 챗GPT, 구글 시대 엔드게임의 서막일까?’라는 제목의 칼럼에서 챗GPT의 출현과 2016년 MS 챗봇 테이의 16시간 만의 운영 중단 사건을 언급하면서 2023년 관전 포인터로 구글링시대에서 챗지피팅(ChatGPTing) 시대로 전환하는 변곡점이 될지 한번 지켜보자고 했다. 출시 1개월여 지난 당시 SNS상에서 챗GPT 열풍이 대단했지만 이렇게 빨리 우리의 일상으로 들어올지 몰랐던 것이다. 출시 3개월이 지난 현재 사회·경제·문화·과학·산업·교육 등 거의 전 분야에 걸쳐 챗지피팅 판도라의 상자가 열렸다.
[사이언스칼럼] 초거대 AI 언어모델 챗GPT, 구글 시대 엔드게임의 서막일까?
Published:
지난 한 달여 동안 글로벌 IT 업계와 SNS를 떠들썩하게 하고 있는 것이 있다. 초거대 AI 언어 생성 모델 GPT-3.5기반 대화형 챗봇인 ‘챗GPT’의 출현이다. 챗GPT 관련 많은 얘기가 세간에 회자되고 있다. 지난 11월 30일에 공개된 지 “5일 만에 시범서비스 사용자 수 100만 명을 돌파했다”고 한다. 이는 넷플릭스 3.5년, 페이스북 10개월, 인스타그램 2.5개월에 비해 가히 엄청난 열풍이다. 영국 일간지 인디펜던트의 12월 3일자 “구글은 끝났다”(Google is done)라는 도발적인 기사도 챗GPT에 대한 호기심을 부채질했다.
[사이언스칼럼] 디지털 대한민국과 슈퍼컴퓨터
Published:
지난 9월 28일에 과학기술정보통신부는 광주에서 열린 대통령 주재 제8차 비상경제 민생회의에서 ‘대한민국 디지털 전략’을 발표했다. 디지털 전환시대에 디지털 추격 국가가 아닌 디지털 혁신 모범 선도 국가가 되겠다는 정부의 강력한 의지 표명이다. 5대 추진 전략과 19개 세부 과제를 제시했다. 필자의 눈길을 끈 것은 첫 번째 추진 전략 ‘세계 최고의 디지털 역량’ 확보를 위한 구체적인 세부 과제로 인공지능(AI), 양자 등 6대 디지털 혁신 기술 연구개발 집중투자와 신경망처리장치(NPU)·슈퍼컴·초거대 인공지능 모델 등 세계 최고 수준의 인공지능기반을 구축을 하겠다는 것이다.
[사이언스칼럼] 고성능컴퓨팅(HPC)기반 국가 디지털인프라 구축
Published:
지난 3일 과학기술정보통신부는 기상·기후, 재난·재해, 나노·소재 등 7개 분야에 걸쳐 초고성능컴퓨팅 전문센터를 선정했다. 엑사컴퓨팅 시대로의 전환 등에 대응해 작년 5월 부총리 주재 비상경제 중앙대책본부회의에서 발표한 ‘국가 초고성능컴퓨팅 혁신전략’의 후속 조치의 일환이다. 분야별 전문센터 설립은 10대 초고성능컴퓨터 활용 전략 분야를 선정해서 국내 초고성능컴퓨터 활용을 강화한다는 3대 정책 방향 중의 하나다.
[사이언스칼럼] 美 ‘프론티어’ 슈퍼컴퓨터, 드디어 엑사스케일 시대를 열다
Published:
지난 10년 동안의 미·중·일 엑사스케일 컴퓨터 개발 경쟁은 미국의 승리로 끝났다. 5월 말에 독일 함부르크에서 열린 국제 슈퍼컴퓨팅 콘퍼런스(ISC2022)에서 미 에너지부(DOE)산하 오크리지국립연구소(ORNL) 프론티어(Frontier)가 지난 2년 동안 슈퍼컴퓨팅 왕좌를 지켜왔던 일본의 후카쿠(Fugaku)를 제치고 슈퍼컴퓨터 톱500 1위에 오른 것이다. 톱500 성능 수치인 HPL(High Performance Linpack)에서 1.1엑사플롭스(EF, 1초에 100경 번 연산)의 성능을 달성함으로 세계 최초 엑사스케일 컴퓨터라는 영예도 안았다.
[사이언스칼럼] 미 국가과학기술위원회 핵심유망기술목록과 첨단컴퓨팅 정책
Published:
지난 2월 미 백악관 국가과학기술위원회(National Science and Technology Council)는 핵심유망기술목록(Critical and Emerging Technologies List Update)을 발표했다. 핵심유망기술(CET)은 미국의 안보와 연관된 첨단 기술 목록으로서 미국의 국가 안보 혁신 기반 촉진 및 기술 우위 보호를 골자로 2020년 10월에 처음 제시됐는데, 이번에 업데이트된 것이다. 2020년 제시된 각 기술 항목에 세부 기술 항목들이 제시됐다.
[사이언스칼럼] 초거대 AI 시대, 국가 슈퍼컴퓨팅 능력 이대로 안된다
Published:
2020년 5월 오픈AI에서 3000억 개의 데이터 셋과 1750억 개의 매개변수를 가진 ‘GPT-3’ 발표를 계기로 초거대 AI 시대의 막이 열렸다. 초거대 AI는 뇌에서 뉴론 간 정보 전달을 담당하는 시냅스 역할을 하는 매개변수의 수가 수 천억 개다. 최근 ‘조’ 단위의 언어 모델이 속속 등장하고 있다. 현재 구글, 화웨이, 마이크로소프트(MS) 등 글로벌 빅테크 기업들의 초거대 AI 모델 개발 경쟁이 치열하다.
[사이언스칼럼] 중국 엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨터에 대한 소문
Published:
지난 11월 중순 미국 세인트루이스에서 슈퍼컴퓨팅 콘퍼런스(SC2021)가 열렸다. 이번 톱 500순위 발표에서 1초에 100경 번 연산이라는 엑사스케일 시대의 서막을 알리는 슈퍼컴퓨터의 탄생을 내심 기대하고 있었다. 기대와는 달리 최상위 순위에 별로 변동이 없었다. 약 450 페타플롭스(PF)의 일본의 후가쿠 시스템이 2020년 6월부터 네 번 연속 슈퍼컴퓨터 왕좌의 자리를 지켰다. 하지만 중국에 두 대의 엑사급 슈퍼컴퓨터가 있다는 소문이다.
[사이언스칼럼] 국가 R&D 디지털자산, 우리도 페어(FAIR) 운동을 벌이자
Published:
2019년 국가 연구개발(R&D) 예산이 20조 원을 넘은 이후 내년에는 30조 원에 육박할 것이라고 한다. 디지털 전환 시대에 이처럼 막대한 국가 예산이 투입된 R&D 디지털 산출물 활용에 대한 국가 차원의 관리가 점점 중요해지고 있다. 2016년 네이처 자매지인 사이언티픽 데이터(Scientific Data)를 통해 산·학·연 50여 명의 저자가 “공공 예산이 투입된 연구 산출물의 공유와 재사용을 위한 페어(FAIR) 원칙”을 주창했다. 연구 산출물은 학술논문·연구데이터·소프트웨어 등 디지털 자산을 망라한다. 페어 원칙이란 “디지털 자산은 찾을 수 있고(Findable), 접근 가능하고(Accessible), 상호운용 가능하며(Interoperable), 재사용할 수 있어야(Reusable)한다”는 4가지 지침을 말한다.
[사이언스칼럼] 국가 디지털 인프라 정책: 민간클라우드 대 공공슈퍼컴퓨팅
Published:
지난 6월 말에 국제 슈퍼컴퓨팅 콘퍼런스(ISC2021)가 온라인으로 개최됐다. 매년 6월과 11월에 열리는 국제 슈퍼컴퓨팅 콘퍼런스의 백미는 슈퍼컴퓨터 톱500 순위 발표다. 이번 톱500에서 필자의 눈에 띈 것은 마이크로소프트사(MS)의 애저 클라우드 시스템 네 개가 26위부터 29위까지에 나란히 등재된 것이다. 현재 아마존 EC2 인스턴스 클러스터도 톱500 40위에 등재돼 있지만, 이는 특정 기업에 구축된 아마존 사설 클라우드 시스템이다. 데이터센터 범용 클라우드 시스템이 톱500에 등재된 것은 이번이 처음이다.
[사이언스칼럼] 국가초고성능컴퓨팅 혁신전략과 국가 AI 백년대계
Published:
지난달 28일 부총리 주재 비상경제 중앙대책본부회의에서 ‘국가초고성컴퓨팅 혁신전략’이 발표됐다. 엑사컴퓨팅 시대로의 전환, 각 국의 기술 안보 강화, 국내 수요 급증 등 급변하는 국내외 초고성능컴퓨팅 환경에 대응해 10년간의 중장기 실천 전략을 담고 있다. 2030년까지 세계 5위 슈퍼컴퓨터 구축, 24개 선도 기술, 엑사급 슈퍼컴퓨터 자체 개발, 소재·나노 등 10대 초고성능컴퓨터 활용 전략 분야를 선정하는 등 인프라·기술개발·활용이라는 3가지 정책 방향으로 추진된다. 2011년에 미국이 이어 세계에서 두 번째로 초고성능컴퓨터법이 제정된 이후 10년 만에 국가 차원의 혁신전략이 나온 셈이다. 다소 늦은 감은 있지만 참으로 다행스런 일이다. 국가 AI 백년대계 관점에서 이번 혁신전략의 의의에 대해서 한번 생각해보자.
[사이언스칼럼] 엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨터 구축이 시급하다
Published:
인공지능(AI) 산업은 오일 산업에 자주 비유된다. 오일 산업에서 원유의 채굴과 정제를 통해서 수많은 석유화학제품이 나오듯이 인공지능 산업에서 데이터는 수집과 기계가 학습할 수 있도록 가공된 후에 학습과 추론을 통해서 수많은 AI 제품과 서비스가 나온다. 지난 2019년 7월 5일자 필자의 칼럼 ‘인공지능의 핵심 인프라 슈퍼컴퓨터와 미중 패권전쟁’에서 AI 기술 혁신에 있어 고성능컴퓨팅(High Performance Computing·HPC)의 역할에 대해서 언급했다.
[사이언스칼럼] 스마트시티와 슈퍼컴퓨터
Published:
2018년 초 세종 5-1생활권과 부산 에코델타시티가 국가시범 스마트시티로 선정됐다. 5G·인공지능·자율주행·가상현실 등 첨단 신기술을 실제로 구현하고, 이를 통해 축적한 스마트시티 기술을 해외에 수출하겠다는 정부의 야심찬 계획이다. 15년 이상 장기적인 혁신서비스를 안정적으로 제공할 민관 합동 사업법인(SPC)으로 세종은 LG CNS 컨소시엄, 부산은 우선협상대상자로 한화에너지 컨소시엄이 지난해 말 선정되는 등 국가시범 도시 구축이 본격적으로 추진되고 있다. 백지부지에서 출발한 국가시범 도시가 첨단 디지털 기술이 융합된 세계적 스마트시티의 선도모델로 탄생되기를 기대한다.
[사이언스칼럼] 코로나19 팬데믹과 슈퍼컴퓨터
Published:
작년 12월에 중국에서 발생한 코로나19 바이러스 감염자 수가 6천만 명을 넘었다. 2002년 사스 감염자 8천여명, 2012년 메르스 감염자 약 2500명에 비하면 그 숫자가 가히 천문학적이다. 독감 철과 맞물린 제3차 대유행으로 유럽의 거의 모든 나라가 한시적인 봉쇄조치를 취하고 있다. 미국도 최근 일주일 확진자 수가 백만 명이 넘는 등 전 세계적인 확산세가 심상치 않다. 반가운 소식은 미국 화이자, 모더나 그리고 영국의 아스트라제네카 등에서 개발 중인 백신들이 임상 3상 시험 막바지 단계에서 좋은 결과를 보이고 있어 한두 주 내로 코로나19 백신이 공식 출시될 것으로 기대된다.
[사이언스칼럼] 디지털뉴딜과 슈퍼컴퓨터
Published:
지난 9월 디지털 뉴딜의 핵심 과제인 ‘데이터 댐’의 7대 사업을 수행할 기업들이 선정되면서 데이터 댐 사업이 본격적으로 시작됐다. 데이터 댐의 핵심은 민간과 공공 데이터를 5G와 같은 고속의 네트워크를 통해 대량으로 수집하고 이를 가공·거래·활용해 인공지능(AI) 기술 기반의 혁신적인 서비스 개발로 기존 산업을 혁신하고 일자리를 창출하는 데 있다. 정부는 필요한 컴퓨팅 인프라로 민간 클라우드를 활용하기로 하고 클라우드 플래그십과 클라우드 바우처 사업 등을 추진하고 있다.
[사이언스칼럼] 일본 9년 만에 슈퍼컴퓨터 1위 탈환, 그 의미와 전망
Published:
코로나19 때문에 온라인으로 열렸던 지난 6월의 국제슈퍼컴퓨팅학회(ISC)에서 일본 이화학연구소(RIKEN)와 후지쯔가 공동 개발한 ‘후가쿠’ 시스템이 세계 슈퍼컴퓨터 순위에서 1위 자리에 등극했다. 지난 2년간 세계 슈퍼컴퓨터 순위에서 1위 자리를 굳건히 지키고 있던 미국 오크리지국립연구소(ORNL)의 ‘서밋’ 시스템을 정상의 자리에서 끌어 내린 것이다. 사실 전통적 슈퍼컴퓨터 강국인 일본이 이번에 슈퍼컴퓨터 왕좌를 차지한 것은 그리 놀라운 일은 아니다. 2002년 6월 ‘어스 시뮬레이터’, 2011년 6월 ‘케이’로 세계 슈퍼컴퓨터 순위인 ‘TOP500’에서 1위를 차지했으니 일본은 지난 20여년 동안 9년마다 슈퍼컴퓨터 순위에서 1위에 오른 셈이다.
[사이언스칼럼] 코로나19 참전에 나선 글로벌 슈퍼컴퓨터들
Published:
지난해 말 중국 의사 리원량에 의해 처음으로 세상에 알려진 신종 코로나바이러스는 전 세계로 급속히 확산돼 4월 중순 현재 전 세계 코로나19 확진자 수는 200만, 사망자 수는 12만 명을 넘어섰다. 한국과 대만 등 몇몇 나라를 제외하면 이미 지역사회 전파 단계에 접어들어 경로가 파악되지 않는 감염자가 속출하고 있다. 이에 대부분의 국가는 사회·경제적으로 큰 고통이 따르는 이동 금지 등 강제적인 봉쇄정책을 펴고 있다. 동시에 “첫째도 테스트, 둘째도 테스트”라며 코로나19 검진에 총력을 기울이고 있다. 이번 코로나19 사태에 대해서 한국의 방역 모델인 ‘신속하고 광범위한 검진을 통한 감염자 정밀 추적’이 전 세계적으로 인정받게 된 것이 참으로 자랑스럽다.
[사이언스칼럼] 2020년 슈퍼컴퓨팅 어디로 갈 것인가
Published:
2020년 슈퍼컴퓨팅 풍향계는 어디를 가리킬 것인가? 첫째, 슈퍼컴퓨터 핵심 엔진인 프로세서 선택의 폭이 인텔 x86 중심에서 점점 다변화될 것으로 예상된다. 특히 ARM 프로세서 기반 슈퍼컴퓨터들이 본격적으로 등장하기 시작할 것이다. 이미 지난해 11월 덴버에서 열린 슈퍼컴퓨팅 컨퍼런스에서 ARM기반 슈퍼컴퓨터로서 일본 후지쯔의 A64FX 프로토타입과 미국 샌디아국립연구소 아스트라가 톱 500 순위에 각각 159위와 198위를 차지했다.
[사이언스칼럼] 우리도 이제 자체 프로세서 기반 슈퍼컴퓨터 개발에 뛰어들 때다
Published:
지난 9월 5일자 필자의 칼럼에서 엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨터 개발을 둘러싼 미•중•일 3국의 경쟁이 치열한 가운데 드디어 EU도 프로세서 기술 독립을 선언하고 엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨터 개발 경쟁에 가세하였다고 언급했다. 우리나라도 이제는 자체 프로세서 기반 슈퍼컴퓨터 구축에 대해서 한번 심각하게 고민해야 할 시점이 아닐까라고 하면서 칼럼을 마무리했었다. 결론적으로 말해서 우리도 더 늦기 전에 자체 프로세서 기반 슈퍼컴퓨터를 개발할 시점이 되었다.
[사이언스칼럼] 미·중·일 엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨터 개발 전쟁 치열
Published:
이르면 2020년에는 엑사스케일(초당 100경 번 연산) 슈퍼컴퓨터가 세상에 데뷔할 것으로 보인다. 지난 수 년 동안 치열한 경쟁을 벌이고 있는 미·중·일 3 국 중에 과연 어느 나라가 최초의 엑사급 슈퍼컴퓨터 개발의 영예를 차지할까? 벌써부터 엑사급 슈퍼컴퓨터 이름들이 속속 나오고 있다. 미국의 오로라(Aurora), 프론티어(Frontier), 엘카피탄(El Capitan), 중국의 선웨이 엑사스케일(Sunway Exascale), 텐허-3(Tainhe-3), 슈광(Shuguang), 그리고 일본의 후가쿠(Fugaku)가 향후 1-2년 내에 세상에 나오게 될 엑사급 슈퍼컴퓨터 후보들이다.
[사이언스칼럼] 인공지능의 핵심 인프라 슈퍼컴퓨터와 미중 패권전쟁
Published:
6월 29일 오사카 G20 미중 정상회담에서 양국은 추가 관세를 더 이상 매기지 않기로 하는 등 무역협상을 재개하기로 하였다. 지난 몇 달 동안 미중 관계는 무역전쟁을 넘어 패권전쟁으로 치닫고 있는 양상이었다. 지난 5월 미국은 세계 최대의 통신장비 제조업체인 중국 화웨이에 대해 무역거래 제한조치를 취했다. 그리고 지난주 G20 회담을 앞두고 중국 최대 슈퍼컴퓨터 업체인 중커수광과 우시 장난 컴퓨터 기술연구소 등을 미국의 거래제한 조치 대상에 포함 시켰다. 이로써 1초에 100경 번의 연산이 가능한 엑사급 슈퍼컴퓨터를 2020년까지 개발하겠다는 중국의 야심찬 계획에도 차질이 불가피할 것으로 보인다. 미국의 이번 슈퍼컴퓨터 관련 핵심 부품의 대 중국 수출 금지 조치의 이유가 미국에서 볼 때 중국의 슈퍼컴퓨터 기술이 장차 미국의 안보에 위협이 될 수 있기 때문이라고 한다.
[사이언스칼럼] 슈퍼컴퓨터계의 빌보드, 톱500 순위의 기원
Published:
매년 6월과 11월에 각각 유럽과 미국에서 열리는 국제 슈퍼컴퓨팅학회에서 세계에서 제일 빠른 슈퍼컴퓨터 500위까지 순위가 발표된다. 현재, 세계에서 제일 빠른 슈퍼컴퓨터는 미국 오크리지 국립연구소의 ‘서밋(Summit)’이다. 한국의 경우에는 지난 해 11월 개통되어 현재 한창 가동 중인 한국과학기술정보연구원(KISTI)의 ‘누리온’이 13위, 기상청의 ‘누리’와 ‘미리’가 각각 82, 83위, 그리고 국내 공공기관으로서는 기상청에 이어서 세 번째로 기초과학연구원(IBS) ‘알레프’가 445위를 차지하고 있다.
[사이언스칼럼] 30년에 걸친 우리나라 슈퍼컴퓨터 도입의 역사
Published:
지난 2018년 11월 7일은 국가초고성능컴퓨팅센터인 한국과학기술정보연구원에서 국가슈퍼컴퓨터 5호기 개통과 우리나라 슈퍼컴퓨터 도입 30주년 기념식이 열렸던 뜻깊은 날이다. 슈퍼컴퓨터 5호기 ‘누리온’은 2010년 도입된 4호기보다 성능이 무려 70배 이상 빠른 25.7페타플롭스, 즉 1초에 2경5700조 번의 연산이 가능한 세계 10위권의 슈퍼컴퓨터이다. 기존 4호기로는 감히 엄두도 못 냈던 우주의 기원과 정밀한 구조 연구와 같은 초거대 계산과학연구는 물론, 4차 산업혁명 시대의 핵심인 빅데이터 분석과 인공지능 연구 등 국가 연구개발 전반에 걸쳐 혁신적인 가치를 창출해 나갈 것으로 그 기대가 크다.
events
International Conference on High Performance Computing in Asia-Pacific Region (HPC Asia 2021)
Published:
Held online on January 20 - 22 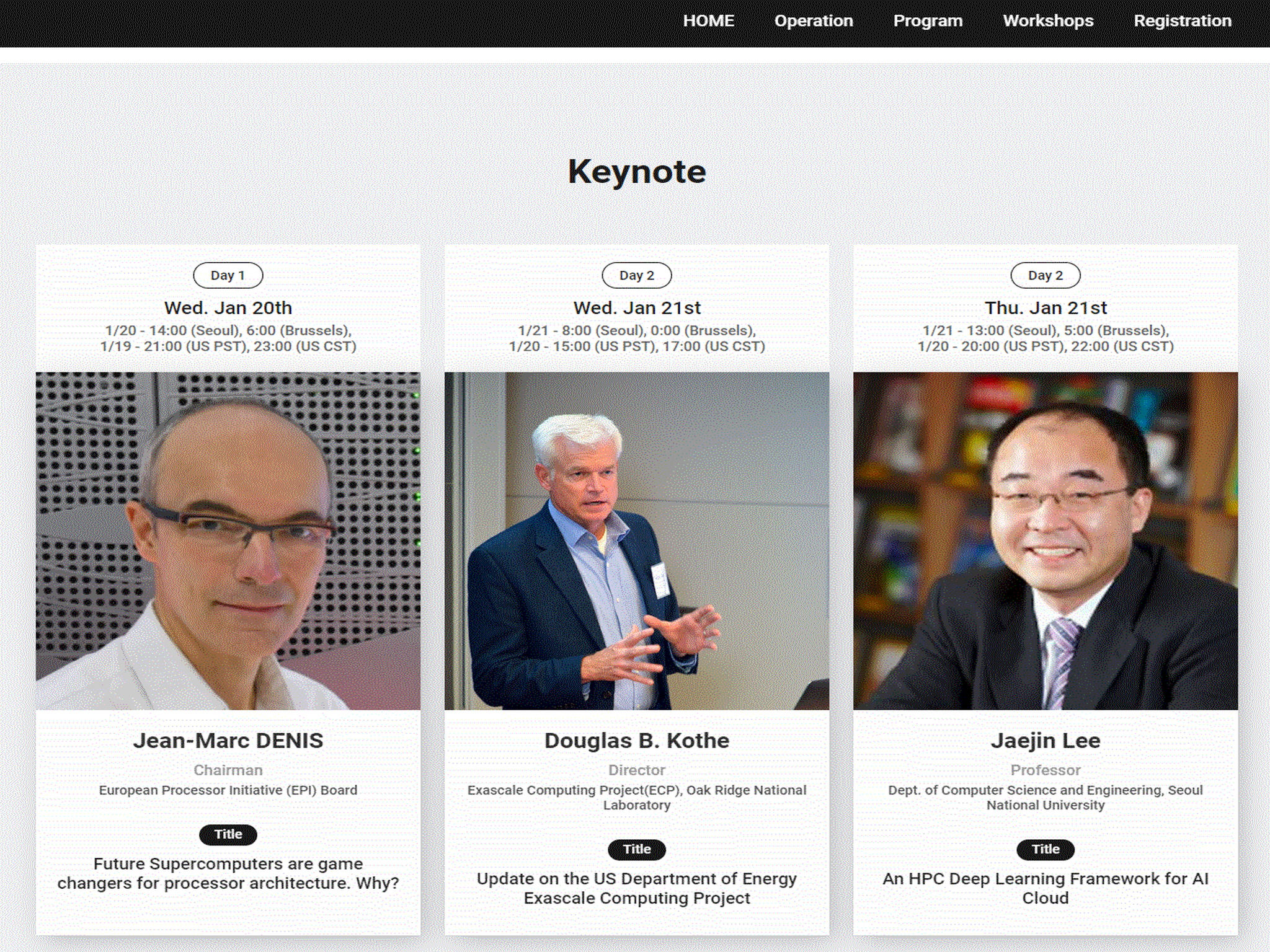
2022 HPC Summer Workshop
Published:
Held in Seoul National University Hoam Faculty House on July 21 
2023 HPC Summer Workshop
Published:
Held in Seoul Shilla Hotel on August 18 
2024 HPC Summer Workshop
Published:
Held in Sogang University on July 30 
2025 HPC Summer Workshop
Published:
Held in Sogang University on July 15 
portfolio
Best Paper Award
Published:
September 2017, IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing (CLUSTER) 
Coursera Certificate
Published:
August 2023, Completion Certificate for Generative AI with Large Language Models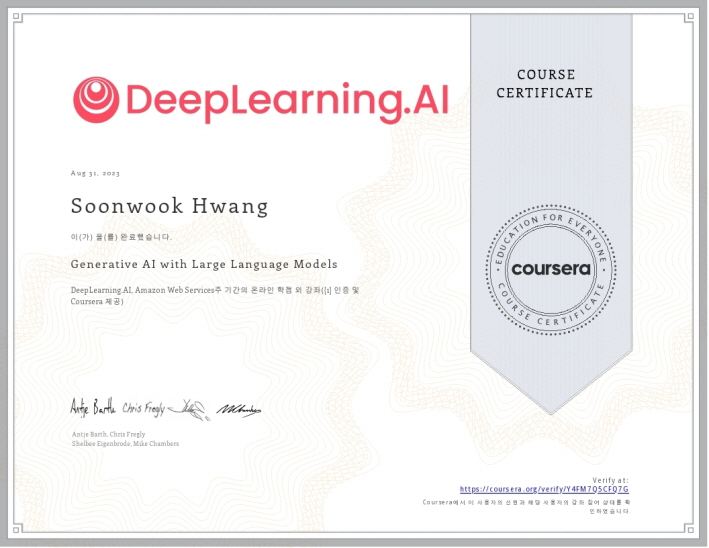
Coursera Certificate
Published:
December 2024, Completion Certificate for Introduction to Generative AI for Software Development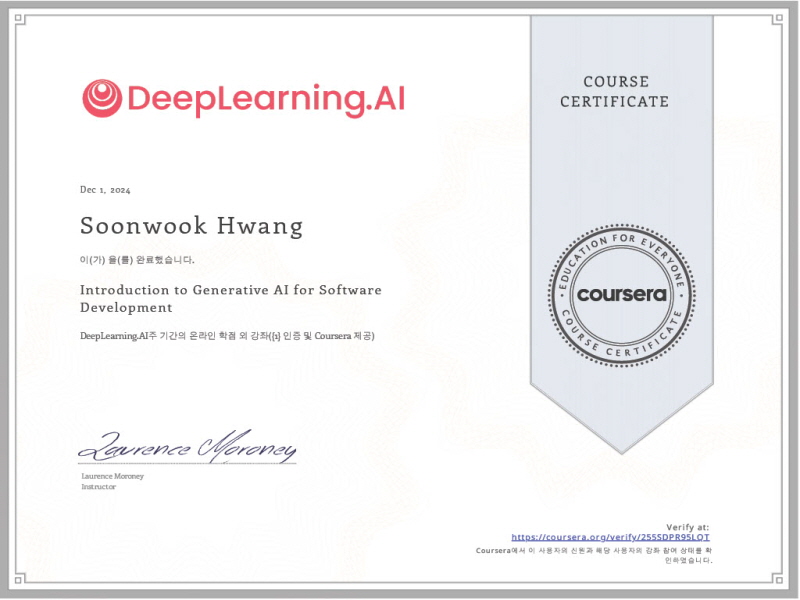
Coursera Certificate
Published:
December 2024, Completion Certificate for Team Software Engineering with AI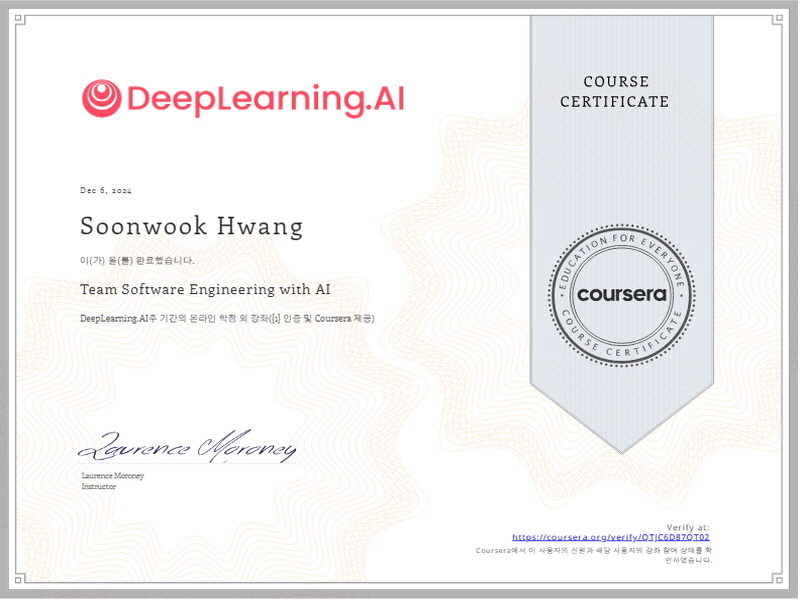
Coursera Certificate
Published:
December 2024, Completion Certificate for AI-Powered Software and System Design
Coursera Certificate
Published:
December 2024, Generative AI for Software Development
Coursera Certificate
Published:
December 2024, AI Infrastructure and Operations Fundamentals
Coursera Certificate
Published:
January 2025, Python Essentials for MLOps
Coursera Certificate
Published:
January 2025, Vertex AI: Qwik Start
NVIDIA Certificate
Published:
September 2025, Fundamentals of Accelerated Computing with Modern CUDA C++
publications
Paper Title Number 1
Published in Journal 1, 2009
This paper is about the number 1. The number 2 is left for future work.
Recommended citation: Your Name, You. (2009). "Paper Title Number 1." Journal 1. 1(1).
Download Paper | Download Slides
Paper Title Number 2
Published in Journal 1, 2010
This paper is about the number 2. The number 3 is left for future work.
Recommended citation: Your Name, You. (2010). "Paper Title Number 2." Journal 1. 1(2).
Download Paper | Download Slides
Paper Title Number 3
Published in Journal 1, 2015
This paper is about the number 3. The number 4 is left for future work.
Recommended citation: Your Name, You. (2015). "Paper Title Number 3." Journal 1. 1(3).
Download Paper | Download Slides
Paper Title Number 4
Published in GitHub Journal of Bugs, 2024
This paper is about fixing template issue #693.
Recommended citation: Your Name, You. (2024). "Paper Title Number 3." GitHub Journal of Bugs. 1(3).
Download Paper
recommendation
Recommdation Letter from Satoshi Sekiguchi
Published:
…My qualifications for recommending Dr. Hwang are based on my expertise as a leader in the field of Grid Computing for many years. As the founding Director of the Grid Technology Research Center (2002-2008) within the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), an Independent Administrative Institution under the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), Japan; I collaborated with Dr. Hwang in the National Research Grid Initiative (NAREGI) project in Japan from 2003. After he moved to KISTI, I continued to form a long-term partnership between AIST and KISTI, and I have interacted with Dr. Hwang on many occasions, including at HPC, AI, and high-speed networks…
Recommdation Letter from Vincent Breton
Published:
…I had the opportunity to get to know Doctor Hwang when I initiated the creation of the France-Korea Particle Physics Laboratory (FKPPL) in 2007….As leader of KISTI Supercomputing/Grid/Cloud-related Research and Development Projects, Soonwook Hwang participated and gave talks regularly to European grid conferences and worshops, strengthening KISTI European collaboration and visibility. … KISTI engineers under Soonwook Hwang supervision contributed major developments to the first large scale drug discovery initiatives on international grid infrastructures. Their efforts paved the way to KISTI important contributions to the EGEE and EGI-InSPIRE European projects. Pioneering virtual screening computing experiments contributed to the identification of potential new drugs against malaria, avian flu and SRAS resulting in several patents.
Recommdation Letter from Dan Reed
Published:
…I have watched Dr. Hwang emerge as one of the world’s foremost leaders in computational science and high-performance computing (HPC). He is widely respected as a researcher in HPC, reflected not only by his publication record in international conferences and journals, but also by his participation and leadership in the global HPC community. He is one of the “go to” individuals for insights and perspectives, not only about advanced computing developments in Asia, but as a thoughtful shaper of global HPC policies and technology practices. His leadership in KISTI’s deployment of advanced computing systems has also elevated KISTI’s profile…
Recommdation Letter from Horst Simon
Published:
…I know Dr. Hwang well and have interacted with him for many years. Based on my collaboration with Dr. Hwang, I can make several observations, that all demonstrate that he is an exemplary researcher. He is very quick in assimilating new technology and insights, and bringing them to bear on established problems. He has far reaching interests, and surveys the literature widely, often coming up with very intriguing new ideas. And lastly, he is always interested in applications, and enjoys working on practical problems. Dr. Hwang combines research excellence with a deep interest in applications. … Since 2006 Dr. Hwang has been leading supercomputing development at KISTI, a distinguished national academic HPC institution worldwide. Because of his leadership KISTI has recovered a leading position in the TOP500 list for which I am an editor. The introduction of the Nurion system in 2018 was a major accomplishment for KISTI and Dr. Hwang. This system ranked #11 on the TOP500 list, which is an appropriate location for the national system of a high tech country such as South Korea…
talks
엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨팅 시대를 맞으며
Published:
슈퍼컴퓨터의 성능은 지속적으로 발전해서 메가, 기가, 테타,를 넘어 이제는 엑사, 즉 1초에 100경번의 연산이 가능한 “꿈의 컴퓨터”인 엑사스케일 컴퓨팅 시대가 논 앞에 다가왔습니다. 수년 전부터 미국, 중국, 일본간의 치열한 엑사스케일 컴퓨팅 경쟁을 벌여 왔습니다. 올 여름 일본이 450페타급 후가쿠 시스템을 구축하여서 엑사시스템에 한층 더 다가왔습니다. 내년이면 미국 오크리지 국립연구소에 ‘프론티어’라는 세계 최초의 엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨터가 구축될 예정이어서 이제 본격적으로 엑사스케일 슈퍼컴퓨팅 시대를 맞이하게 됩니다. 본 강연은 최근 글로벌 슈퍼컴퓨팅 구축 및 기술 동향과 한국의 슈퍼컴퓨팅 역사와 현황에에 대해서 조망하고자 합니다.
멀티 GPU 노드 기반 분산 딥러닝 튜토리얼
Published:
Distributed Deep Learning (DDL) training refers to the process of training a deep learning model on multiple machines, possibly with multiple GPUs on each machine. Not only does DDL training speed up the training process, but also enables the use of larger models and datasets that could not fit on a single GPU. This tutorial is intended to guide users to run his/her distributed deep learning codes on multiple GPU nodes using Horovod on Neuron. Neuron is a KISTI GPU cluster consisting of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs). Horovod, originally developed by Uber in 2017, is a distributed deep learning framework aiming to make it easy and simple to take a DL code developed with different DL frameworks such as Tensorflow and Pytorch and scale it to run across many GPUs. This tutorial will also give a short demo of how to practice large-scale distributed deep learning training using Horovod on Perlmutter, the world 9th fastest supercomptuer, which is located at NERSC supercomputing center in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Using Multiple GPUs for Distributed Deep Learning on Neuron
Published:
Distributed deep learning (DDL) training refers to the process of training a deep learning model on multiple machines, possibly with multiple GPUs on each machine. Not only does DDL training speed up the training process, but also enables the use of larger models and datasets that could not fit on a single GPU. This tutorial is intended to guide users to run his/her distributed deep learning codes on multiple GPU nodes using Horovod on Neuron. Neuron is a KISTI GPU cluster consisting of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs). Horovod, originally developed by Uber in 2017, is a distributed deep learning framework aiming to make it easy and simple to take a DL code developed with different DL frameworks such as Tensorflow and Pytorch and scale it to run across many GPUs.
슈퍼컴퓨터에서 멀티 GPU노드기반 분산딥러닝하기
Published:
Distributed deep learning (DDL) training refers to the process of training a deep learning model on multiple machines, possibly with multiple GPUs on each machine. Not only does DDL training speed up the training process, but also enables the use of larger models and datasets that could not fit on a single GPU. This tutorial is intended to guide users to run his/her distributed deep learning codes on multiple GPU nodes using Horovod on Neuron. Neuron is a KISTI GPU cluster consisting of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs). Horovod, originally developed by Uber in 2017, is a distributed deep learning framework aiming to make it easy and simple to take a DL code developed with different DL frameworks such as Tensorflow and Pytorch and scale it to run across many GPUs. This tutorial will also give a short demo of how to practice large-scale distributed deep learning training using Horovod on Perlmutter, the world 9th fastest supercomptuer, which is located at NERSC supercomputing center in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
슈퍼컴퓨터에서 멀티노드기반 분산딥러닝하기
Published:
Distributed deep learning (DDL) training refers to the process of training a deep learning model on multiple machines, possibly with multiple GPUs on each machine. Not only does DDL training speed up the training process, but also enables the use of larger models and datasets that could not fit on a single GPU. This talk is intended to introduce the principles, concepts and approaches of large-scale distributed DL practices on a supercomputer, and guide users to run his/her distributed deep learning codes on multiple GPU nodes using Horovod on Neuron. Neuron is a KISTI GPU cluster consisting of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs). Horovod, originally developed by Uber in 2017, is a distributed deep learning framework aiming to make it easy and simple to take a DL code developed with different DL frameworks such as Tensorflow and Pytorch and scale it to run across many GPUs.
슈퍼컴퓨터에서 멀티노드기반 분산딥러닝하기
Published:
Distributed deep learning (DDL) training refers to the process of training a deep learning model on multiple machines, possibly with multiple GPUs on each machine. Not only does DDL training speed up the training process, but also enables the use of larger models and datasets that could not fit on a single GPU. This talk is intended to introduce the principles, concepts and approaches of large-scale distributed DL practices on a supercomputer, and guide users to run his/her distributed deep learning codes on multiple GPU nodes using Horovod on Neuron. Neuron is a KISTI GPU cluster consisting of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs). Horovod, originally developed by Uber in 2017, is a distributed deep learning framework aiming to make it easy and simple to take a DL code developed with different DL frameworks such as Tensorflow and Pytorch and scale it to run across many GPUs. This talk will also give a short demo of how to practice large-scale distributed deep learning training using Horovod on Perlmutter, the world 9th fastest supercomptuer, which is located at NERSC supercomputing center in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
슈퍼컴퓨터에서 멀티 GPU노드기반 분산딥러닝하기
Published:
Distributed deep learning (DDL) training refers to the process of training a deep learning model on multiple machines, possibly with multiple GPUs on each machine. Not only does DDL training speed up the training process, but also enables the use of larger models and datasets that could not fit on a single GPU. This tutorial is intended to share best practices for large-scale distributed training on a supercomputer, guiding users on how to run their distributed deep learning codes on multiple GPU nodes using Horovod on Neuron. The Neuron system is a KISTI GPU cluster consisting of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs). Horovod, originally developed by Uber in 2017, is a distributed deep learning framework aiming to make it easy and simple to take a DL code developed with different DL frameworks such as Tensorflow and Pytorch and scale it to run across many GPUs. This tutorial will also give a short demo of how to practice large-scale distributed deep learning training using Horovod on Perlmutter, the world 9th fastest supercomptuer, which is located at NERSC supercomputing center in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
슈퍼컴퓨터에서 멀티노드기반 분산딥러닝하기
Published:
최근에 구축되는 Top10 슈퍼컴퓨터들은 한 노드에 최신 GPU 4~8개를 장착하고 있다. 본 세션에서는 슈퍼컴퓨터에서의 멀티 GPU노드를 활용한 대규모 분산딥러닝하기 Best Practices를 소개한다. (1)슈퍼컴퓨터에 접속해서 (2)각자의 가상 환경을 만들고 (3)온라인으로 GPU 1~2개를 할당받아 터미널 또는 주피터 환경에서 분산딥러닝 코드를 개발 및 테스트 한 후에 (4)배치 작업을 통해서 대규모 분산딥러닝 작업을 실행하는 슈퍼컴퓨터에서의 AI/DL 연구프로세스에 대해서 공유하고 의견을 나누고자 한다.
Best Practices for Generative AI with LLMs on a Supercomputer
Published:
Generative AI with LLMs refers to the use of large language models like GPT-3 for generating human-like content, spanning text, images and even code. LLMs are trained on a vast amount of data and code, and usually carefully prompt-engineered or fine-tuned to suit specific downstream tasks such as Chatbots, Translation, Question Answering and Summarization. The contents and python codes of this tutorial are originated from the 16-hour “Generative AI with LLMs” course offered by the DeepLearning.AI. This tutorial will mainly cover the key concepts and practices of a typical LLM-powered Generative AI lifecycle, from data gathering and model selection, to instruction fine-tuning and RLHF-based alignment to human preference, to performance evaluation and deployment. For hands-on exercises, students will have access to the KISTI GPU cluster known as Neuron, which consists of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs) running SLURM as for its workload manager.
Best Practices for Generative AI with LLMs on a Supercomputer
Published:
Generative AI with LLMs refers to the use of large language models like GPT-3 for generating human-like content, spanning text, images and even code. LLMs are trained on a vast amount of data and code, and usually carefully prompt-engineered or fine-tuned to suit specific downstream tasks such as Chatbots, Translation, Question Answering and Summarization. The contents and python codes of this seminar are mainly originated from the 16-hour “Generative AI with LLMs” course offered by the DeepLearning.AI. This talk will cover the key concepts and practices of a typical LLM-powered Generative AI lifecycle, from data gathering and model selection, to instruction fine-tuning and RLHF-based alignment to human preference, to performance evaluation and deployment. I will show a short demo on how users can create a conda virtual environment on the KISTI Neuron cluster with 260 GPUs, launch a Jupyter server on a compute node and have access it to from his/her own PC or Labtop for Genera tive AI practices on a supercomputer. The demo will illustrate how to conduct LLM practices including prompting and prompt engineering, and instruction fine-tuning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) with LoRA, and evaluation and benchmark on LLMs.
Best Practices for Generative AI with LLMs on a Supercomputer
Published:
Generative AI with LLMs refers to the use of large language models like GPT-3 for generating human-like content, spanning text, images and even code. LLMs are trained on a vast amount of data and code, and usually carefully prompt-engineered or fine-tuned to suit specific downstream tasks such as Chatbots, Translation, Question Answering and Summarization. The contents and python codes of this seminar are mainly originated from the 16-hour “Generative AI with LLMs” course offered by the DeepLearning.AI. This talk will cover the key concepts and practices of a typical LLM-powered Generative AI lifecycle, from data gathering and model selection, to instruction fine-tuning and RLHF-based alignment to human preference, to performance evaluation and deployment. I will show a short demo on how users can create a conda virtual environment on the KISTI Neuron cluster with 260 GPUs, launch a Jupyter server on a compute node and have access it to from his/her own PC or Labtop for Genera tive AI practices on a supercomputer. The demo will illustrate how to conduct LLM practices including prompting and prompt engineering, and instruction fine-tuning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) with LoRA, and evaluation and benchmark on LLMs.
Best Practices for Generative AI with LLMs on a Supercomputer
Published:
Generative AI with LLMs refers to the use of large language models like GPT-3 for generating human-like content, spanning text, images and even code. LLMs are trained on a vast amount of data and code, and usually carefully prompt-engineered or fine-tuned to suit specific downstream tasks such as Chatbots, Translation, Question Answering and Summarization. The contents and python codes of this tutorial are originated from the 16-hour “Generative AI with LLMs” course offered by the DeepLearning.AI. This tutorial will mainly cover the key concepts and practices of a typical LLM-powered Generative AI lifecycle, from data gathering and model selection, to instruction fine-tuning and RLHF-based alignment to human preference, to performance evaluation and deployment. For hands-on exercises, students will have access to the KISTI GPU cluster known as Neuron, which consists of 65 nodes with 260 GPUs (120 of NVIDIA A100 and 140 of NVIDIA V100 GPUs) running SLURM as for its workload manager.
Best Practices for Generarive AI with LLMs on a Supercomputer
Published:
본 세션에서는 슈퍼컴퓨터에서 “LLM 기반 생성형 AI 해보기”의 Best Practice를 소개합니다. 데이터 수집, 모델 선택, 프롬프트 엔지니어링, 인스트럭션 파인튜닝, 평가 및 벤치마킹 등 생성형 AI 프로젝트 라이프사이클 전 과정을 살펴보고, KISTI GPU 클러스터에 접속해서 시연을 진행합니다. 특히, 슈퍼컴퓨터와 AWS 같은 클라우드 플랫폼 환경을 비교하고, SLURM 기반슈퍼컴퓨터 환경에서 주피터 노트북을 활용한 생성형 AI 실습 사례를 공유합니다.
Evolution of LLMs and AI Agents: From Transformer to DeepSeek-R1 to Manus AI
Published:
In this talk, I present an overview of the evolving landscape of Large Language Models (LLMs), tracing their progression from the introduction of the Transformer in 2017 to the latest developments like DeepSeek-R1 in 2025. The talk reflects on this evolution, particularly in terms of the types of training datasets and approaches, including pretraining, Supervised/Instruction Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It also delves into the rise of Agentic AI during 2025, featuring key technologies such as Manus AI and Model Context Protocol (MCP). The presentation includes hands-on demonstrations showcasing the creation of basic AI agents using GPTs, Claude+MCP, and n8n.
Evolution of LLMs and AI Agents: From Transformer to DeepSeek-R1 to Manus AI
Published:
In this talk, I present an overview of the evolving landscape of Large Language Models (LLMs), tracing their progression from the introduction of the Transformer in 2017 to the latest developments like DeepSeek-R1 in 2025. The talk reflects on this evolution, particularly in terms of the types of training datasets and approaches, including pretraining, Supervised/Instruction Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It also delves into the rise of Agentic AI during 2025, featuring key technologies such as Manus AI and Model Context Protocol (MCP). The presentation includes hands-on demonstrations showcasing the creation of basic AI agents using GPTs, Claude+MCP, and n8n.
Evolution of LLMs and AI Agents: From Transformer to DeepSeek-R1 to Manus AI
Published:
In this talk, I present an overview of the evolving landscape of Large Language Models (LLMs), tracing their progression from the introduction of the Transformer in 2017 to the latest developments like DeepSeek-R1 in 2025. The talk reflects on this evolution, particularly in terms of the types of training datasets and approaches, including pretraining, Supervised/Instruction Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). It also delves into the rise of Agentic AI during 2025, featuring key technologies such as Manus AI and Model Context Protocol (MCP). The presentation includes hands-on demonstrations showcasing the creation of basic AI agents using GPTs, Claude+MCP, and n8n.
A Deep Dive into Distributed Training of Large-scale Language Modeling with PyTorch on a Supercomputer
Published:
This tutorial presents a comprehensive, in-depth guide for large-scale distributed training of LLMs on supercomputers managed with SLURM. It briefly covers some basics of collective communications in message passing including gather, scatter and all-gather operations, delving into data parallelism techniques such as Data Parallelism (DP) and Distributed Data Parallelism (DDP) in PyTorch, and model parallelism techniques including Tensor Parallelism, Pipeline Parallelism, and 3D Parallelism, with hands-on PyTorch code examples. It also covers how to set up and leverage distributed training tools like NVIDIA Megatron-LM and Microsoft DeepSpeed to efficiently run the PyTorch codes using multiple GPUs on a supercomputer.
teaching
Teaching experience 1
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Teaching experience 2
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
